Engineering plastics
Materials for automotive millimeter wave radar antennas
XYRON™ XP650 (AA105-52)/DG040
- Electronics
- Others

Marketing Areas
- ALL
XYRON™ XP650 (AA105-52) and DG040 have high heat resistance and a stable low coefficient of linear expansion over a wide temperature range, making them suitable for resinifying metal parts that require high precision, such as slotted waveguide array antenna.
Feature
- Improved antenna performance
- Reduction of processing cost
- Better dimensional stability
Usage
- Millimeter wave radar antennas
- ADAS
- Drone
Engineering plastics
Materials for automotive millimeter wave radar antennas
XYRON™ XP650 (AA105-52)/DG040
Asahi Kasei proposes forming waveguides using metal-plated modified PPE resin XYRON™ to reduce weight and manufacturing costs while maintaining performance.
Asahi Kasei proposes forming waveguides using metal-plated modified PPE resin XYRON™ to reduce weight and manufacturing costs while maintaining performance.
Improved antenna performance
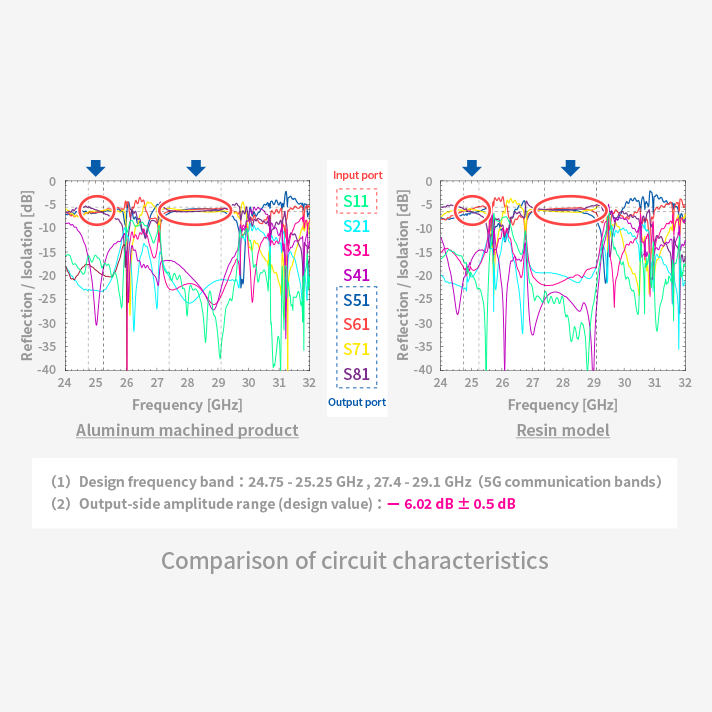
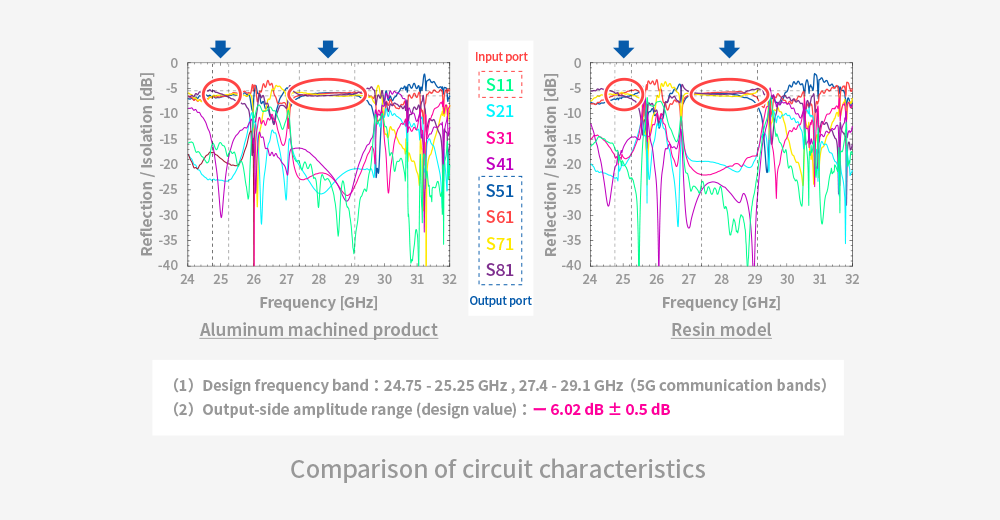
Waveguide antennas made with metal-plated XYRON™ offer improved antenna performance compared to conventional microstrip antennas by utilizing air—the material with the lowest dielectric constant—as the waveguide medium.
Reduction of processing cost
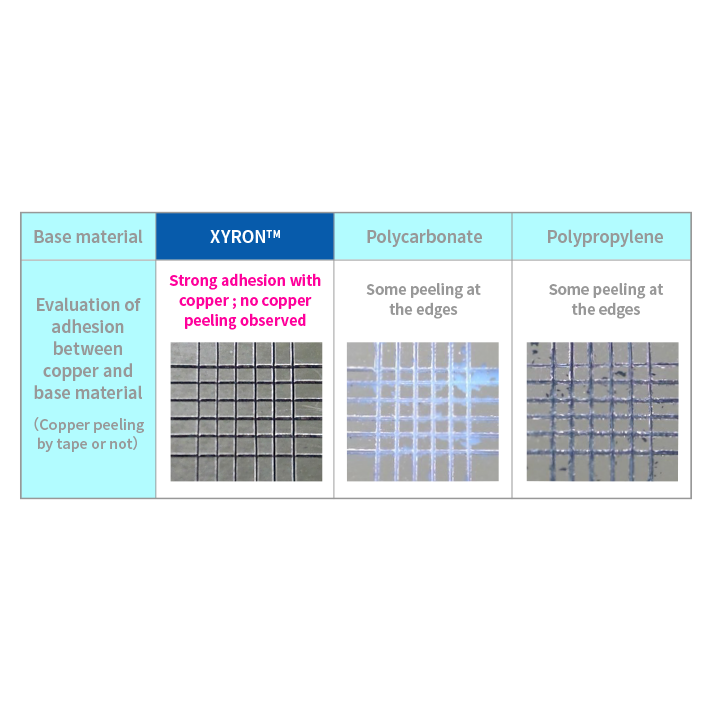
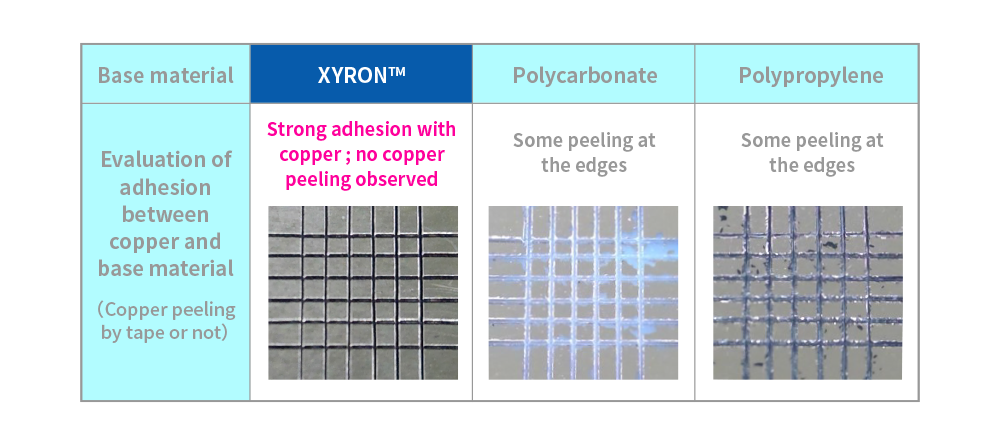
The development of slotted waveguide array antenna often faces cost-related challenges. By utilizing waveguide antennas plated with XYRON™, it is possible to reduce metal processing costs and enable mass production. In addition, XYRON™ supports wet plating similar to ABS and, unlike PPS and other resins, does not require any special pretreatment. This simplifies the plating process and contributes to further cost reduction.
Better dimensional stability
XYRON™ offers low warpage, high dimensional accuracy, and excellent mold replication, enabling superior shape reproducibility. These properties make it well-suited for resin substitution of metal components that require high precision, such as slotted waveguide array antenna.
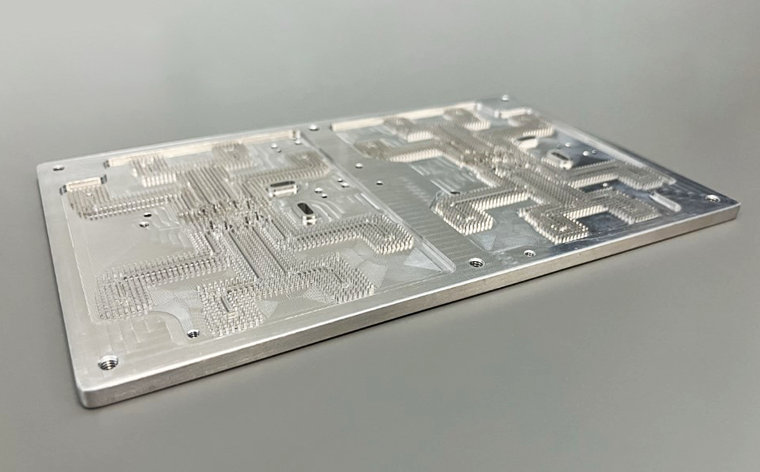
Slotted waveguide array antenna

Slotted waveguide array antennas are millimeter-wave band antennas that typically have a structure where multiple slot antenna elements are provided in a metal waveguide to operate as an array antenna. These antennas have recently been considered for applications such as ADAS due to their high performance.
Asahi Kasei and the Hirokawa Laboratory at Institute of Science Tokyo (formerly Tokyo Institute of Technology) are working to reduce the weight and manufacturing costs of slotted waveguide array antenna by forming the waveguide out of metal-plated XYRON™ XP650 (AA105-52).
 Mobility-related information website
Mobility-related information website